Performance Analysis of Data Encryption Algorithms
Abdel-Karim Al Tamimi, aa7@wustl.edu
Abstract
The two main characteristics that identify and differentiate one encryption algorithm from another are its ability to secure the protected data against attacks and its speed and efficiency in doing so. This paper provides a performance comparison between four of the most common encryption algorithms: DES, 3DES, Blowfish and AES (Rijndael). The comparison has been conducted by running several encryption settings to process different sizes of data blocks to evaluate the algorithm's encryption/decryption speed. Simulation has been conducted using C# language.Keywords : Encryption Algorithm, Performance,Analysis, AES, DES, Blowfish, TripleDES, Cryptography
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Cryptography : Overview
- Related Work Results
- Simulation Setup
- Performance Evaluation Methodology
- Simulation Results
- Conclusion
- References
- Acronyms
See Also : Security in Wireless Data Networks , Network Security Concepts: Review
1. Introduction
As the importance and the value of exchanged data over the
Internet or other media types are increasing, the search for the best solution
to offer the necessary protection against the data thieves' attacks along with
providing these services under timely manner is one of the most active subjects
in the security related communities.
This paper tries to present a fair comparison between the
most common and used algorithms in the data encryption field. Since our main
concern here is the performance of these algorithms under different settings,
the presented comparison takes into consideration the behavior and the
performance of the algorithm when different data loads are used.
Section 2 will give a quick overview of cryptography and its
main usages in our daily life; in addition to that it will explain some of the
most used terms in cryptography along with a brief description of each of the
compared algorithm to allow the reader to understand the key differences between
them.Section 3 will show the results achieved by other contributions and their
conclusions. Section 4 will walk through the used setup environment and settings
and the used system components. Section 5 illustrates the performance evaluation
methodology and the chosen settings to allow a better comparison. Section 6
gives a thorough discussion about the simulation results, and finally section 7
concludes this paper by summaries the key points and other related
considerations.
2. Cryptography: Overview
An overview of the main goals behind using cryptography will
be discussed in this section along with the common terms used in this field.
Cryptography is usually referred to as "the study of
secret", while nowadays is most attached to the definition of encryption.
Encryption is the process of converting plain text "unhidden" to a cryptic text
"hidden" to secure it against data thieves. This process has another part where
cryptic text needs to be decrypted on the other end to be understood. Fig.1
shows the simple flow of commonly used encryption algorithms.
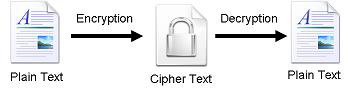
Fig.1 Encryption-Decryption Flow
As defined in RFC 2828
[RFC2828], cryptographic system is "a set of cryptographic algorithms
together with the key management processes that support use of the algorithms in
some application context." This definition defines the whole mechanism that
provides the necessary level of security comprised of network protocols and data
encryption algorithms.
2.1 Cryptography Goals
This section explains the five main goals behind using Cryptography.
Every security system must provide a bundle of security functions that can assure the secrecy of the system. These functions are usually referred to as the goals of the security system. These goals can be listed under the following five main categories[Earle2005]:
Authentication: This means that before sending and receiving data using the system, the receiver and sender identity should be verified.
Secrecy or Confidentiality: Usually this function (feature) is how most people identify a secure system. It means that only the authenticated people are able to interpret the message (date) content and no one else.
Integrity: Integrity means that the content of the communicated data is assured to be free from any type of modification between the end points (sender and receiver). The basic form of integrity is packet check sum in IPv4 packets.
Non-Repudiation: This function implies that neither the sender nor the receiver can falsely deny that they have sent a certain message.
Service Reliability and Availability:
Since secure systems usually get attacked by intruders, which may affect their
availability and type of service to their users. Such systems should provide a
way to grant their users the quality of service they expect.
2.2 Block Ciphers and Stream Ciphers
One of the main categorization methods for encryption
techniques commonly used is based on the form of the input data they operate on.
The two types are Block Cipher and Stream Cipher. This section discusses the
main features in the two types, operation mode, and compares between them in
terms of security and performance.
Before starting to describe the key characteristics of block cipher, the definition of cipher word must be presented. "A cipher is an algorithm for performing encryption (reverse is decryption) "[Wikipedia-BC].
In this method data is encrypted and decrypted if data is in from of blocks. In its simplest mode, you divide the plain text into blocks which are then fed into the cipher system to produce blocks of cipher text.
ECB(Electronic Codebook Mode) is the basic form of clock
cipher where data blocks are encrypted directly to generate its correspondent
ciphered blocks (shown in Fig. 2). More discussion about modes of operations
will be discussed later.
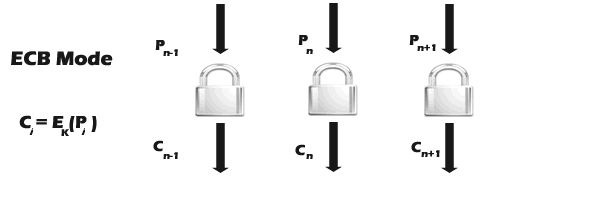
Fig.2 Block Cipher ECB Mode.
Stream cipher functions on a stream of data by operating on
it bit by bit. Stream cipher consists of two major components: a key stream
generator, and a mixing function. Mixing function is usually just an XOR
function, while key stream generator is the main unit in stream cipher
encryption technique. For example, if the key stream generator produces a series
of zeros, the outputted ciphered stream will be identical to the original plain
text. Figure 3 shows the operation of the simple mode in stream cipher.
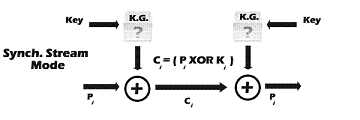
Fig. 3 Stream Cipher (Simple Mode)
2.3 Mode of Operations
This section explains the two most common modes of operations in Block Cipher encryption-ECB and CBC- with a quick visit to other modes.
There are many variances of block cipher, where different techniques are used to strengthen the security of the system. The most common methods are: ECB (Electronic Codebook Mode), CBC (Chain Block Chaining Mode), and OFB (Output Feedback Mode). ECB mode is the CBC mode uses the cipher block from the previous step of encryption in the current one, which forms a chain-like encryption process. OFB operates on plain text in away similar to stream cipher that will be described below, where the encryption key used in every step depends on the encryption key from the previous step.
There are many other modes like CTR (counter), CFB (Cipher Feedback), or 3DES specific modes that are not discussed in this paper due to the fact that in this paper the main concentration will be on ECB and CBC modes.
2.4 Symmetric and Asymmetric encryptions
Data encryption procedures are mainly categorized into two categories depending on the type of security keys used to encrypt/decrypt the secured data. These two categories are: Asymmetric and Symmetric encryption techniques
In this type of encryption, the sender and the receiver agree
on a secret (shared) key. Then they use this secret key to encrypt and decrypt
their sent messages. Fig. 4 shows the process of symmetric cryptography. Node A
and B first agree on the encryption technique to be used in encryption and
decryption of communicated data. Then they agree on the secret key that both of
them will use in this connection. After the encryption setup finishes, node A
starts sending its data encrypted with the shared key, on the other side node B
uses the same key to decrypt the encrypted messages.
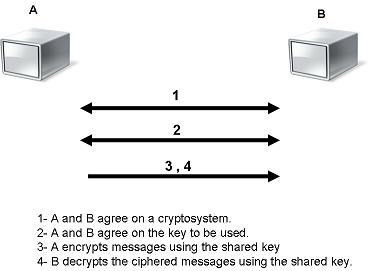
Fig.4 Symmetric Encryption
The main concern behind symmetric encryption is how to share the secret key
securely between the two peers. If the key gets known for any reason, the whole
system collapses. The key management for this type of encryption is troublesome,
especially if a unique secret key is used for each peer-to-peer connection, then
the total number of secret keys to be saved and managed for n-nodes will be
n(n-1)/2
[Edney2003] .
Asymmetric encryption is the other type of encryption where two keys are
used. To explain more, what Key1 can encrypt only Key2 can decrypt, and vice
versa. It is also known as Public Key Cryptography (PKC), because users tend to
use two keys: public key, which is known to the public, and private key which is
known only to the user. Figure 5 below illustrates the use of the two keys
between node A and node B. After agreeing on the type of encryption to be used
in the connection, node B sends its public key to node A. Node A uses the
received public key to encrypt its messages. Then when the encrypted messages
arrive, node B uses its private key to decrypt them.
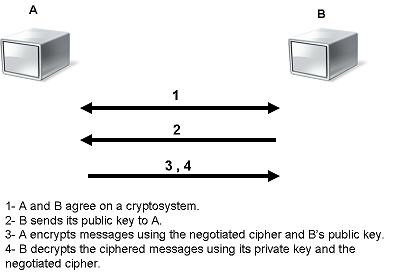
Fig.5 Asymmetric Encryption
This capability surmounts the symmetric encryption problem of managing secret keys. But on the other hand, this unique feature of public key encryption makes it mathematically more prone to attacks. Moreover, asymmetric encryption techniques are almost 1000 times slower than symmetric techniques, because they require more computational processing power[Edney2003] [ Hardjono2005] .
To get the benefits of both methods, a hybrid technique is usually used. In this technique, asymmetric encryption is used to exchange the secret key, symmetric encryption is then used to transfer data between sender and receiver.
2.5 Compared Algorithms
This section intends to give the readers the necessary background to understand the key differences between the compared algorithms.
DES: (Data Encryption Standard), was the first encryption standard to be recommended by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology). It is based on the IBM proposed algorithm called Lucifer. DES became a standard in 1974 [TropSoft] . Since that time, many attacks and methods recorded that exploit the weaknesses of DES, which made it an insecure block cipher.
3DES: As an enhancement of DES, the3DES (Triple DES) encryption standard was proposed. In this standard the encryption method is similar to the one in original DES but applied 3 times to increase the encryption level. But it is a known fact that 3DES is slower than other block cipher methods.
AES: (Advanced Encryption Standard), is the new encryption standard recommended by NIST to replace DES. Rijndael (pronounced Rain Doll) algorithm was selected in 1997 after a competition to select the best encryption standard. Brute force attack is the only effective attack known against it, in which the attacker tries to test all the characters combinations to unlock the encryption. Both AES and DES are block ciphers.
Blowfish:
It is one of the most common public domain encryption algorithms provided by
Bruce Schneier - one of the world's leading cryptologists, and the president of
Counterpane Systems, a consulting firm specializing in cryptography and computer
security.
Blowfish is a variable length key, 64-bit block cipher. The
Blowfish algorithm was first introduced in 1993.This algorithm can be optimized
in hardware applications though it's mostly used in software applications.
Though it suffers from weak keys problem, no attack is known to be successful
against [BRUCE1996][Nadeem2005].
In this section a brief description of the compared encryption algorithms have been introduced. This introductions to each algorithm are to provided the minimum information to distinguish the main differences between them.
To give more prospective about the performance of the
compared algorithms, this section discusses the results obtained from other
resources.
One of the known cryptography libraries is Crypto++
[Crypto++]. Crypto++ Library is a free C++ class library of cryptographic
schemes. Currently the library consists of the following, some of which are
other people's code, repackaged into classes.
Table 1 contains the speed benchmarks for some of the most commonly used cryptographic algorithms. All were coded in C++, compiled with Microsoft Visual C++ .NET 2003 (whole program optimization, optimize for speed, P4 code generation), and ran on a Pentium 4 2.1 GHz processor under Windows XP SP 1. 386 assembly routines were used for multiple-precision addition and subtraction. SSE2 intrinsics were used for multiple-precision multiplication.
It can be noticed from the table that not all the modes have
been tried for all the algorithms. Nonetheless, these results are good to have
an indication about what the presented comparison results should look like.
Also it is shown that Blowfish and AES have the best
performance among others. And both of them are known to have better encryption
(i.e. stronger against data attacks) than the other two.
| Algorithm | Megabytes(2^20 bytes) Processed | Time Taken | MB/Second |
| Blowfish | 256 | 3.976 | 64.386 |
| Rijndael (128-bit key) | 256 | 4.196 | 61.010 |
| Rijndael (192-bit key) | 256 | 4.817 | 53.145 |
| Rijndael (256-bit key) | 256 | 5.308 | 48.229 |
| Rijndael (128) CTR | 256 | 4.436 | 57.710 |
| Rijndael (128) OFB | 256 | 4.837 | 52.925 |
| Rijndael (128) CFB | 256 | 5.378 | 47.601 |
| Rijndael (128) CBC | 256 | 4.617 | 55.447 |
| DES | 128 | 5.998 | 21.340 |
| (3DES)DES-XEX3 | 128 | 6.159 | 20.783 |
| (3DES)DES-EDE3 | 64 | 6.499 | 9.848 |
Table 1 Comparison results using Crypto++
[Nadeem2005] In this paper, the popular secret key
algorithms including DES, 3DES, AES (Rijndael), Blowfish, were implemented, and
their performance was compared by encrypting input files of varying contents and
sizes. The algorithms were implemented in a uniform language (Java), using their
standard specifications, and were tested on two different hardware platforms, to
compare their performance.
Tables 2 and 3 show the results of their experiments, where they have
conducted it on two different machines: P-II 266 MHz and P-4 2.4 GHz.
|
Table 2 Comparative execution times (in seconds) of encryption
algorithms in ECB mode on a P-II 266 MHz machine
|
Table 3 Comparative execution times (in seconds) of encryption
algorithms in ECB mode on a P-4 2.4 GHz machine
From the results it is easy to observe that Blowfish has an
advantage over other algorithms in terms of throughput.
[Nadeem2005] has also conducted comparison between the algorithms in stream
mode using CBC, but since this paper is more focused on block cipher the results
were omitted.
The results showed that Blowfish has a very good performance
compared to other algorithms. Also it showed that AES has a better performance
than 3DES and DES. Amazingly it shows also that 3DES has almost 1/3 throughput
of DES, or in other words it needs 3 times than DES to process the same amount
of data.
[Dhawan2002] has also done experiments for comparing the performance of the
different encryption algorithms implemented inside .NET framework. Their results
are close to the ones shown before (Figure 6).
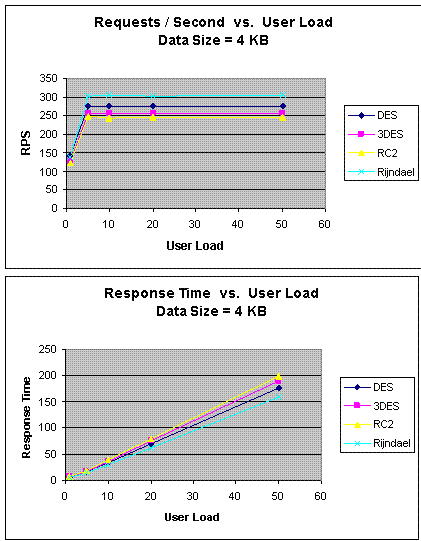
Fig. 6 Comparison results using .NET implemntations[Dhawan2002]
The comparison was performed on the following algorithms:
DES, Triple DES (3DES), RC2 and AES (Rijndael). The results shows that AES
outperformed other algorithms in both the number of requests processes per
second in different user loads, and in the response time in different user-load
situations.
This section gave an overview of comparison results achieved by other people in the field.
4. Simulation Setup
This section describes the simulation environment and the
used system components.
As mentioned this simulation uses the provided classes in
.NET environment to simulate the performance of DES, 3DES and AES (Rijndael).
Blowfish implementation used here is the one provided by Markus Hahn
[BlowFish.NET]
under the name Blowfish.NET. This implementation is thoroughly tested and is
optimized to give the maximum performance for the algorithm.
The implementation uses managed wrappers for DES, 3DES and
Rijndael available in System.Security.Cryptography that wraps unmanaged
implementations available in CryptoAPI. These are DESCryptoServiceProvider,
TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider and RijndaelManaged respectively. There is only a
pure managed implementation of Rijndael available in
System.Security.Cryptography, which was used in the tests.
Table 4 shows the algorithms settings used in this
experiment. These settings are used to compare the results initially with the
result obtained from
[Dhawan2002].
| Algorithm | Key Size
(Bits) |
Block Size
(Bits) |
| DES | 64 | 64 |
| 3DES | 192 | 64 |
| Rijndael | 256 | 128 |
| Blowfish | 448 | 64 |
Table 4 Algorithms settings
3DES and AES support other settings, but these settings
represent the maximum security settings they can offer. Longer key lengths mean
more effort must be put forward to break the encrypted data security.
Since the evaluation test is meant to evaluate the results
when using block cipher, due to the memory constraints on the test machine (1
GB) the test will break the load data blocks into smaller sizes .The load data
are divided into the data blocks and they are created using the
RandomNumberGenerator class available in System.Security.Cryptography namespace.
5. Performance Evaluation Methodology
This section describes the techniques and simulation choices
made to evaluate the performance of the compared algorithms. In addition to
that, this section will discuss the methodology related parameters like: system
parameters, experiment factor(s), and experiment initial settings.
5.1 System Parameters
The experiments are conducted using 3500+ AMD 64bit processor
with 1GB of RAM. The simulation program is compiled using the default settings
in .NET 2003 visual studio for C# windows applications. The experiments will be
performed couple of times to assure that the results are consistent and are
valid to compare the different algorithms.
5.2 Experiment Factors
In order to evaluate the performance of the compared
algorithms, the parameters that the algorithms must be tested for must be
determined.
Since the security features of each algorithm as their
strength against cryptographic attacks is already known and discussed. The
chosen factor here to determine the performance is the algorithm's speed to
encrypt/decrypt data blocks of various sizes.
5.3 Simulation Procedure
By considering different sizes of data blocks (0.5MB to 20MB)
the algorithms were evaluated in terms of the time required to encrypt and
decrypt the data block. All the implementations were exact to make sure that the
results will be relatively fair and accurate.
The Simulation program (shown below in Fig. 7) accepts three
inputs: Algorithm, Cipher Mode and data block size. After a successful
execution, the data generated, encrypted, and decrypted are shown. Notice that
most of the characters can not appear since they do not have character
representation. Another comparison is made after the successful
encryption/decryption process to make sure that all the data are processed in
the right way by comparing the generated data (the original data blocks) and the
decrypted data block generated from the process.
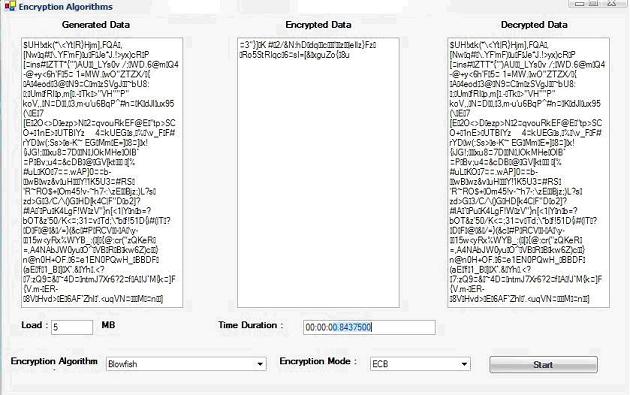
Fig.7 GUI of the simulation program
6. Simulation Results
This section will show the results obtained from running the
simulation program using different data loads. The results show the impact of
changing data load on each algorithm and the impact of Cipher Mode (Encryption
Mode) used.
6.1 Performance Results with ECB
The first set of experiments were conducted using ECB mode,
the results are shown in figure 8 below. The results show the superiority of
Blowfish algorithm over other algorithms in terms of the processing time. It
shows also that AES consumes more resources when the data block size is
relatively big. The results shown here are different from the results obtained
by [Dhawan2002]
since the data block sizes used here are much larger than the ones used in their
experiment.
Another point can be noticed here that 3DES requires always
more time than DES because of its triple phase encryption characteristic.
Blowfish ,although it has a long key (448 bit) , outperformed other encryption
algorithms. DES and 3DES are known to have worm holes in their security
mechanism, Blowfish and AES, on the other hand, do not have any so far.
These results have nothing to do with the other loads on the
computer since each single experiment was conducted multiple times resulting in
almost the same expected result. DES, 3DES and AES implementation in .NET is
considered to be the best in the market.
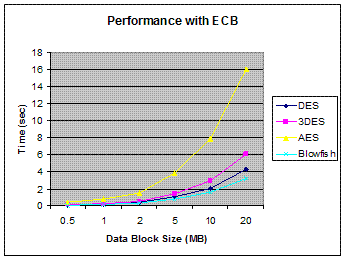
Fig.8 Performance Results with ECB Mode
6.2 Performance Results with CBC
As expected CBC requires more processing time than ECB
because of its key-chaining nature. The results show in Fig. 9 indicates also
that the extra time added is not significant for many applications, knowing that
CBC is much better than ECB in terms of protection. The difference between the
two modes is hard to see by the naked eye, the results showed that the average
difference between ECB and CBC is 0.059896 second, which is relatively small.
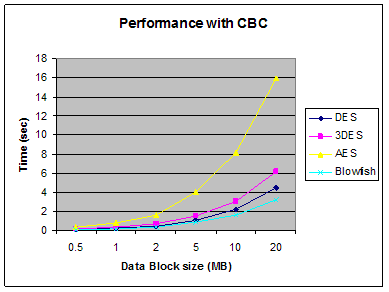
Fig. 9 Performance Results with CBC Mode
This section showed the simulation results obtained by
running the four compared encryption algorithms using different Cipher Modes.
Different load have been used to determine the processing power and performance
of the compared algorithms.
7. Conclusion
The presented simulation results showed that Blowfish has a
better performance than other common encryption algorithms used. Since Blowfish
has not any known security weak points so far, which makes it an excellent
candidate to be considered as a standard encryption algorithm. AES showed poor
performance results compared to other algorithms since it requires more
processing power. Using CBC mode has added extra processing time, but overall it
was relatively negligible especially for certain application that requires more
secure encryption to a relatively large data blocks.
References
- [RFC2828],"Internet Security Glossary", http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/rfc2828.html
- [Nadeem2005]Aamer Nadeem et al, "A Performance Comparison of Data Encryption Algorithms", IEEE 2005
- [Earle2005] "Wireless Security Handbook,". Auerbach Publications 2005
- [Dhawan2002] Priya Dhawan., "Performance Comparison: Security Design Choices," Microsoft Developer Network October 2002. http://msdn2.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms978415.aspx
- [Edney2003]," Real 802.11 Security: Wi-Fi Protected Access and 802.11i ,". Addison Wesley 2003
- [Wikipedia-BC] "Block Cipher", http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Block_cipher
- [Hardjono2005]," Security In Wireless LANS And MANS ,". Artech House Publishers 2005
- [TropSoft] "DES Overview", [Explains how DES works in details, features and weaknesses]
- [Bruce1996] BRUCE SCHNEIER, "Applied Cryptography" , John Wiley & Sons, Inc 1996
- [Crypto++]"Crypto++ benchmark", http://www.eskimo.com/~weidai/benchmarks.html [Results of comparing tens of encryption algorithms using different settings].
- [BlowFish.NET] "Coder's Lagoon",http://www.hotpixel.net/software.html [List of resources to be used under GNU]
Acronyms
| 3DES | Triple Data Encryption Standard |
| AES | Advanced encryption Standard |
| CBC | Chain Block Chaining Mode |
| CTR | Counter Mode |
| CFB | Cipher Feedback Mode |
| ECB | Electronic Codebook Mode |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| OFB | Output Feedback Mode |
| PKC | Public Key Cryptography |